Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is one of the most advanced engineering methods for analyzing fluid behavior. This method uses numerical algorithms and high-performance computers to solve the equations of fluid motion and present precise results in the form of images, graphics, and 3D animations. CFD is used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, energy, and medicine . This article covers the basics of CFD, its advantages and disadvantages, and applications .
1. What is a contract for difference (CFD)?
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of computational fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods such as CFD to simulate the behavior of fluid flow. This method is based on solving the Navier–Stokes equations that describe the motion of fluids .
1.1 Basic steps of numerical flow modeling
-
Geometric modeling:
-
Use CAD software to design a 3D model of a system (e.g., a pipe, an airplane, or a water tank).
-
-
Construction of computer networks (networks):
-
To solve equations numerically, the model is broken down into small elements (grids).
-
-
Let us define the boundary conditions:
-
Velocity, pressure and temperature are applied at the inlet and outlet.
-
-
Solver:
-
Velocity, pressure and temperature fields are calculated using numerical algorithms.
-
-
Post-processing phase:
-
Displays results as graphs, charts, and animations.
-
2. Advantages of using CFDs





3. Disadvantages and problems of numerical fluid mechanics




4. Application of numerical fluid mechanics in various industries
4.1. Aerospace industry
-
Aerodynamic analysis of aircraft and rockets
-
Improve fuel consumption
-
Investigation of the flow around wind turbines
4.2 Automotive industry
-
The body design is optimized to reduce air resistance.
-
Modeling the engine cooling system
-
Cabin airflow analysis
4.3 Oil and gas industry
-
Modeling of flow in pipes
-
Performance analysis of gas-liquid separators
-
Improvement of chemical reactors
4.4 Energy and Environment
-
Design of hydraulic and wind turbine blades
-
Modeling of pollutant emissions into the atmosphere
-
Analysis of the cooling system of a power plant
4.5 Medicine and Biomechanics
-
Modeling of venous blood flow
-
Analysis of the effectiveness of the ventilator
-
Design of medical implants
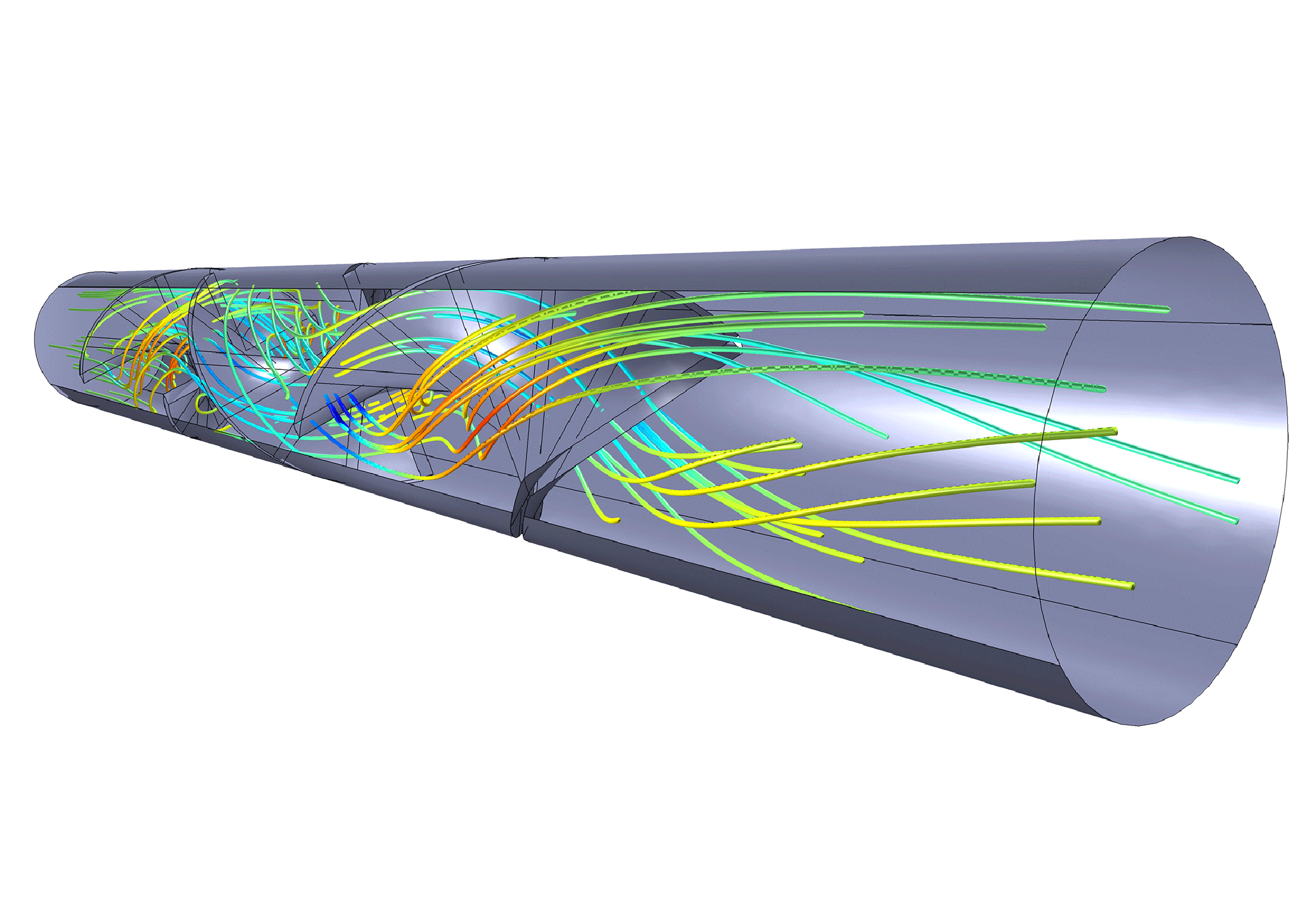
5. Common software for computational fluid mechanics
| programming | Main areas of application |
|---|---|
| ANSYS Fluent | The most comprehensive software for complex modeling |
| COMSOL Multiphysics | Suitable for solving a variety of physical problems. |
| Open foam | Open source software with high customization options |
| Star-CCM+ | User-friendly, cross-disciplinary analysis functions |
| Flow simulation in SolidWorks | Suitable for mechanical engineers. |
6. The future of computational fluid dynamics: machine learning and artificial intelligence
Today, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are changing the methods of computational dynamics:
-
Using neural networks to reduce simulation time
-
Predicting flow patterns without fully solving the equations
-
Automatic design optimization using genetic algorithms
7. Conclusion
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool for analyzing and optimizing fluid systems, reducing costs , and improving design accuracy . Advances in computational fluid dynamics are expanding the scope of CFD. Effective use of this method requires a deep understanding of fluid dynamics, numerical methods, and specialized software .
Keywords: numerical flow modeling, CFD, ANSYS Fluent, Navier-Stokes equations, CFD applications, flow analysis, artificial intelligence in CFD.
If you need advice on numerical flow modeling, please contact our specialists.